





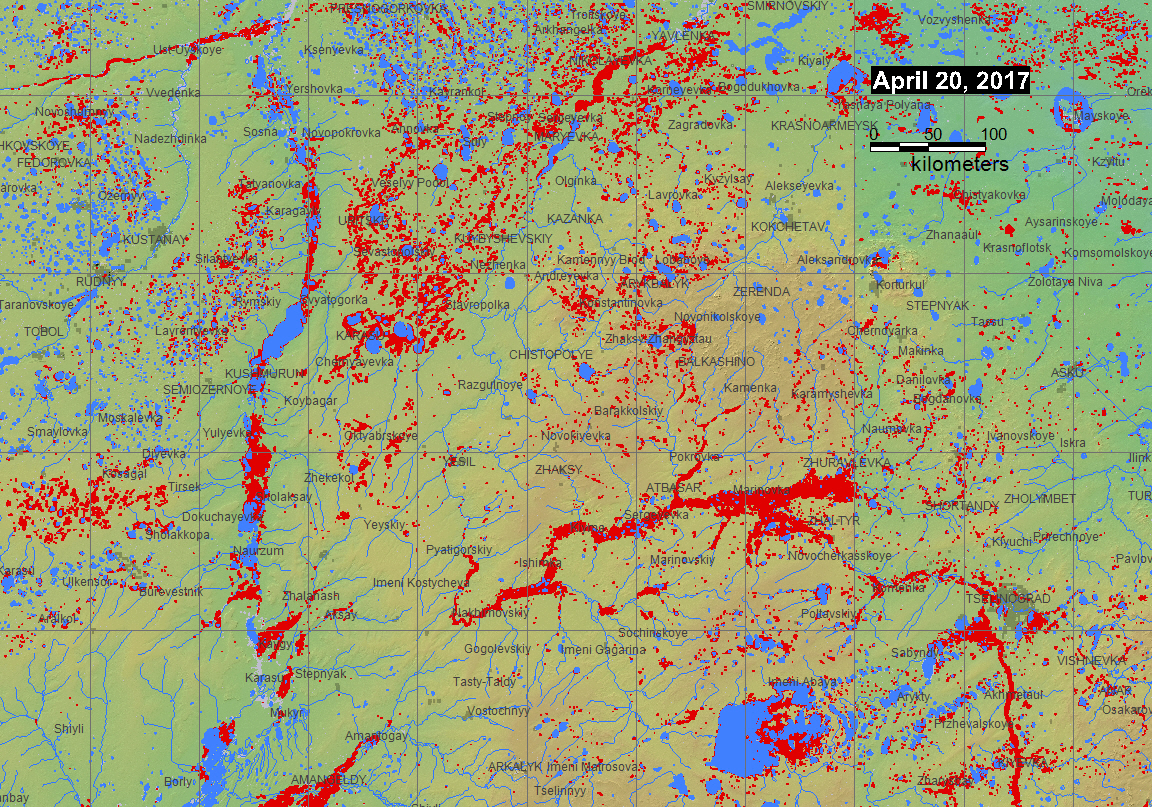
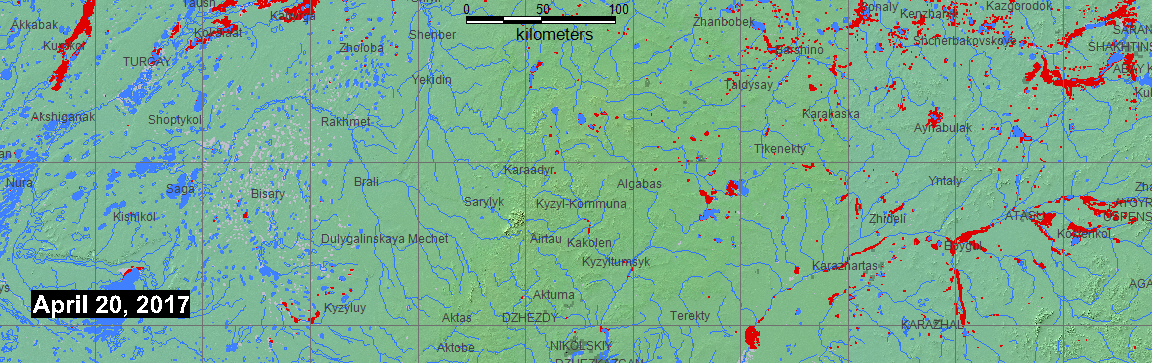
The Flood Observatory maintains a Global Active Archive of large flood events, 1985 to present. It is available to the public in both spreadsheet and GIS formats (both formats together provide the complete Archive). New events are entered into this archive each week. As of the end of 2016, there were 4432 events; each has a unique archive number.
According to the Flood List, April 19, 2017, "Kazakhstan – 7,000 Evacuated After Snowmelt Causes Floods in 7 Regions 19 APRIL, 2017 BY RICHARD DAVIES IN ASIA, NEWS, Flooding has been reported in 7 regions of Kazakhstan over the last few days after snowmelt increased river levels across many parts of the country. The country's Committee for Emergency Situations said that 7,115 people have been evacuated in total after flooding in the regions of Akmola (around 2,000 evacuated), Aktobe, East Kazakhstan, Zhambyl, Karaganda (around 1,500 evacuated), Kostanay and North Kazakhstan (around 1,000 evacuated). At least 70 people had to be rescued from flood water. Emergency teams have pumped flood water and erected temporary flood defence and also helped move livestock to safe areas. The Committee for Emergency Situations says that around 1,500 homes have been damaged, plus some public buildings including a school. Emergency situations have been declared in Aktobe (Aktobe region), Gabit Musrepov district in North Kazakhstan region and Beskaragay district of the East Kazakhstan region. Melting snow caused similar flooding in Kazakhstan during April 2015 when at least 15,000 people were evacuated".
For a web map service version, visit this DFO link and, zoom in to location of interest, and turn on appropriate data layers.
NASA Landsat 8 and ESA Sentinel SAR data if used in this map were obtained from the the U.S. Geological Survey Hazards Data Distribution System. and the Sentinels Science Data hub, respectively. Landsat 8 is jointly managed by NASA and the United States Geological Survey. Flood modeling results if used are from the NASA/University of Maryland Global Flood Monitoring System (GFMS), Drs. Robert Adler and Huan Wu, University of Maryland/ESSIC.
Event-specific water extent files supporting this Flood Event Map are located here. These may include high spatial resolution mapping such as from Sentinel or Landsat, or lower resolution files from MODIS. Draft versions may be posted and later revised; such revisions will include in the file names "r1", "r2", etc. The older files remain in this folder but generally should not be used. Both MapInfo and Shp formats are provided.
Click here for access to the automated daily MODIS-derived .shp file GIS record (record commences in 2011). Where conditions are favorable, this processor provides daily updates of surface water extent. Constraints are primarily: prolonged cloud cover, noise ("false positive" water from cloud and terrain shadows) and also (not detected) very sediment-rich water.
Data from the Global Surface Water Explorer (a download data link is provided) is included as part the (dark blue) surface water layer. It is based on Landsat data at a spatial resolution of 30 m (Jean-Francois Pekel, Andrew Cottam, Noel Gorelick, Alan S. Belward, High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 540, 418-422, 2016). On the map, it is shown together with the NASA Shuttle Water Boundary Data (SWBD) surface water extent (90 m resolution) processed from the 11-day February, 2000, SRTM mission and corrected using Landsat data. Large flood events are not normally depicted in either data set. Thus, red areas on our maps show flood extent beyond these more typical water extents.
When used, NASA NRT Global Flood Mapping maximum water extent for the years 2013-2015, at 250 m spatial resolution, provide part of the (dark blue) maximum flood mapped. DFO creates these annual water extent layers from data provided by that project, by accumulating into one annual file all of the daily .shp files for each year. DFO has also produced flood extent files through mapping of individual floods (~ yr 2000 to present); these are also included where available in this maximum flood extent layer.
(counting since April 21, 2017)